Nos publications scientifiques
FMEA of a non-selective fault-clearing strategy for HVDC grids
The Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a technique used to investigate failures in a process or component and to identify the resultant effects of these failures on system operations. In this paper it is explained how the FMEA can be used to define and assess the impact of the failure modes (FM) of a protection strategy for High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) grids.
Study of the impact of DC-DC converters on the protection strategy of HVDC grids
This paper studies the role of DC-DC converters in the protection of HVDC grids acting as firewalls to stop the propagation of faults. The effects of blocking the converter or actively controlling its operation during faults are presented.The results demonstrate the capabilities of DC-DC converters beyond DC voltage transformation.
Power system stability enhancement via VSC-HVDC control using remote signals: Application on the Nordic 44-bus test system
In this paper the benefits of embedded VSC-HVDC links with supplementary controls for small-signal stability enhancement purposes using remote signals are studied and applied on the Nordic Grid.
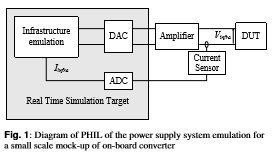
25 kV-50 Hz railway power supply system emulation for Power-Hardware-in-the-Loop testings
This paper presents a methodology to consider the impedance of a grid in power hardware in the loop (PHIL) experiments to validate power converter control in presence of harmonics or resonances in the network impedance. As the phenomena to emulate are in a large frequency range, the skin effect in conductors has to be taken into account. A procedure is developed to model the network.
Dielectric properties of ceramic substrates and current developments for medium voltage applications
Why are ceramic materials (when compared to organic materials) necessary for the purpose of electric isolation in power modules, especially for medium voltage applications...
Modelling of a 25 kV-50 Hz railway infrastructure for harmonic analysis
This paper presents a methodology for the modelling of a 25 kV-50 Hz railway infrastructure, for frequencies from 0 to 5 kHz. It aims to quantify the amplifications of current and voltage harmonics generated by on-board converters into the infrastructure. A circuit is developed to model the skin effect in the overhead line for time-domain simulations. A new approach, based on state space representation and transfer functions, is also proposed to analyse the interactions between trains.
Design of a 1200 V, 100 kW Power Converter: How Good are the Design and Modelling Tools?
During the design of power converter, design mistakes must be avoided, especially for high voltage and high power converters. Simulation tools can be used to help the designers and limit the risks. This presentation will present a design flow approach used to design and validate a 1.2 kV – 100 kW DC-DC converter which was design from die to converter levels and started for a “blank page”. The presentation is organized in four parts. Firstly, the context of the work is introduced. Then, the simulation flow approach used to validate the design is presented. For this part, the presentation will focus on the system level simulation of one inverter, including the power modules. This part will highlight the main limitations of the current simulation tools found by the designers. In the third part, an enhanced approach is proposed to overcome the limitations and the first results are presented Finally, a conclusion will be presented.
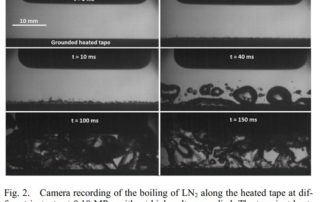
Study of Turn-to-Turn Electrical Breakdown for Superconducting Fault Current Limiter Applications
The rational insulation design of a resistive superconducting fault current limiter (r-SCFCL) requires data gathered from experimental setups representative of the final apparatus. Therefore, an experimental study was performed to characterize the electrical breakdown (BD) of liquid nitrogen (LN2) in the peculiar conditions of a quenching superconducting device.
Arc appearance and cathode spot distribution in a long gap high-current vacuum arc controlled by an external axial magnetic field
An experimental study of a high-current vacuum arc (VA) generated between two static CuCr25 contacts spaced 20 or 30 mm apart was conducted to characterize the arc appearance and the cathode spot (CS) distribution.
Packaging of 10 kV SiC MOSFETs: Trade-Off Between Electrical and Thermal Performances
SiC transistors can achieve blocking voltages of 10kV and more. This makes them especially attractive for energy transmission and distribution. Although SiC devices can in theory operate at high temperature (more than 200°C), the on-state resistance of SiC MOSFETs exhibits a strong dependency on the junction temperature. As a consequence, it is shown that these transistors must actually operate at a relatively low junction temperature (less than 100°C) to increase conversion efficiency and prevent thermal runaway. This requirement for high-performance cooling systems has consequences on the packaging technology: the corresponding power modules must both offer a high voltage insulation and a low thermal resistance. In particular, there is a trade-off in the thickness of the ceramic substrate located between the SiC devices and the cooling system. We propose a new substrate structure, with raised features, which improves the voltage strength of a substrate without increasing its thickness. This structure is demonstrated experimentally.