PhD Justine BILLORE “Thermal aging of XLPE for HVDC cables”
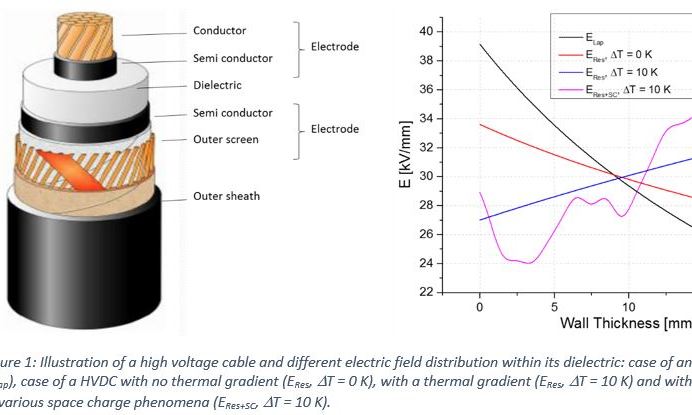
To connect the different points of the network, the transmission and distribution of electric power used cables. Since few years, cables and especially their insulation part are evolving, going from paper insulation to a synthetic insulation. Nowadays, the insulation part of HVDC cables is in crosslinked polyethylene or XLPE.