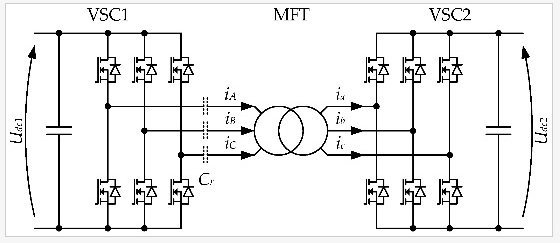
Power electronic traction transformers (PETT) are multilevel AC/DC on-board converters, studied for railway applications to replace traditional solution with low frequency transformers. This paper focuses on the insulated DC/DC converter in a PETT. Three variants of resonant single active bridges (R-SAB) with 3-level NPC primaries are optimised to maximise the efficiency, under mass and dimension constraints. They are sized and compared for a 2 MW PETT on a 15 kV/16.7 Hz railway infrastructure, using 3.3 kV SiC MOSFETs and nanocrystalline C-core transformers with cast resin insulation and forced air cooling. The highest efficiency at nominal power, 99.17 %, is reached for a configuration with a 3-level full bridge NPC primary, a 2-level full bridge secondary, and a 32.1 L/49.1 kg transformer operating at 6 kHz.