Phd Guilherme DANTAS DE FREITAS
“Development of a methodology for DC grid protection strategies comparison”

Abstract
High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) grids are considered a promising solution for problems faced by nowadays power system such as: lines congestion, integration of large amounts of renewable power and enhancement of AC system stability. Among the challenges in the deployment of a HVDC meshed grid, the protection of these grids is regarded as one of the most critical. The protection of HVDC grid is challenging not only because the swift transients and fault currents without zero-crossing, but also due to the impact a DC faults can have on the AC system. Several propositions for HVDC grids protection strategies can be found in literature. Differences between the strategies found are many: protection equipment used, impact on the connected AC system, fault clearing philosophy, technology, etc. Figure 1 gives an idea about all the factors considered in the protection strategy design for a given system.
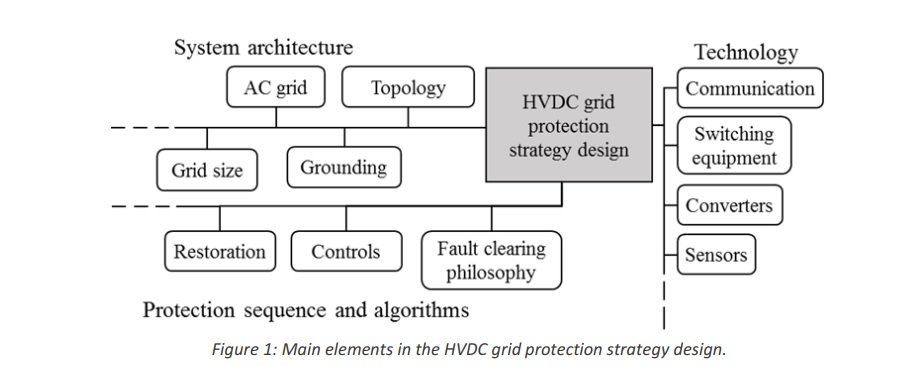
Given the numerous possibilities of protection strategies, a methodology for evaluation and comparison of options for a given system is of utmost importance.
In the literature, studies performing comparison between different HVDC grid protection strategies and the evaluation whether a strategy is acceptable for a given AC/DC system are scarce. The few studies existent are based on the effects/impacts a contingency on the DC grid has on the AC system connected to the HVDC grid. The proposed comparison methodology for protection strategies is based on DC indicators and the risk of the strategy. These two components are combined into the score of the protection strategy.
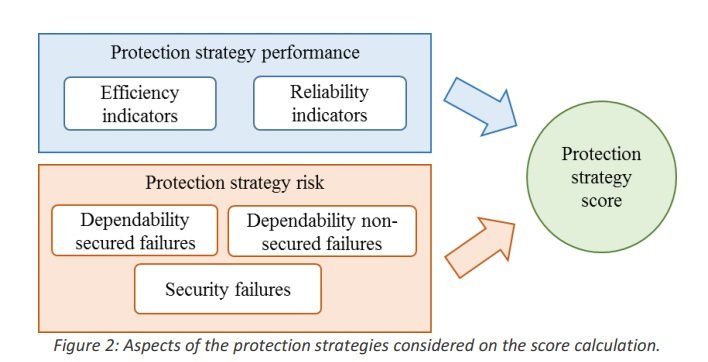
Key Performance Indicators (KPI) are proposed to determine protection strategy performance. Two categories of indicators are defined: efficiency and reliability indicators. The second component of the Score, the risk, is calculated considering the failure modes of the protection strategy. A risk analysis technique adapted from the ISO31000 and using the Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) are used to estimate the risk of the protection strategy. Three protection strategies are evaluated and compared by the proposed methodology. The case studies are implemented in a 4 terminals HVDC grid partially embedded in a standard 2-zone 4-machine AC system.
The protection strategies chosen as case studies are:
- Full-selective strategy using DC Circuit Breakers (DCCBs)
- Non-selective strategy using AC Circuit Breakers (ACCBs)
- Non-selective strategy using DCCBs
The three case studies have their performance assessed and risk analyzed. The execution of these two steps brings several insights about the protection and system analyzed, however the main use of the outputs found is to calculate the score of the strategy. The score each strategy attained is used to rank, according to the considered criteria, the best options for the benchmark HVDC grid protection.
Thesis director: Bertrand Raison (Grenoble INP, University of Grenoble Alpes, G2Elab)
Thesis co-director: Eric Niel (INSA Lyon, Ampere Laboratory)


